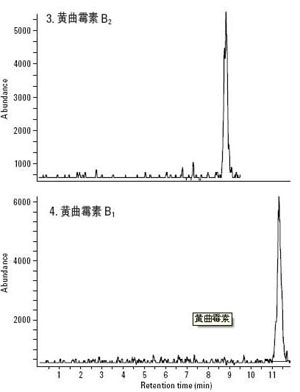
What is aflatoxin? Aflatoxin is a metabolite produced by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. It is highly toxic, and it also has carcinogenic and teratogenic effects. Can cause bones, internal organs and other lesions, and even cancer. Aspergillus flavus is widely found in the soil, so general crops such as peanuts, corn, and rice are susceptible to Aspergillus flavus infection. In addition, nuts such as walnuts and almonds may also contain aflatoxin. The production of aflatoxin not only involves the process of planting but also the processing. Aflatoxin is divided into four types, B1, B2, G1, G2, of which aflatoxin b1 is the most toxic. The MRM chromatograms for these four aflatoxins are described below. Aflatoxin content According to the standard, the allowable amount of aflatoxin in rice and edible oil is 10ug/Kg, and that of other grains, beans, and fermented foods is 5ug/Kg. Baby milk substitutes should not be detected. The maximum allowable amount of aflatoxin recommended by the World Health Organization is 15ug/kg, which is strictly 3 orders of magnitude higher than our national standard. 30 to 50 ua/kg is low toxicity, 50 to 100 ug/kg is toxic, 100 to 1000 ug/kg is highly toxic, and 1000 ug/kg or more is extremely toxic. Its toxicity is 10 times that of potassium cyanide and 68 times that of arsenic. Aflatoxin production factors (in peanuts) Aflatoxin production has the following factors, namely: variety resistance, soil, temperature and moisture, peanut maturity, mechanical damage, storage conditions six factors. The soil factor means that the soil contains a lot of Aspergillus flavus. Different soil types have different rates of infection with Aspergillus flavus. The temperature-water factor means that peanuts are more susceptible to infection with Aspergillus flavus when the temperature is higher and the moisture content is below 35%. The initial temperature of infection by Aspergillus flavus is 25°C-27°C, and the optimum temperature is 28°C-30°C. The degree of drought is proportional to aflatoxin, that is, the more drought, the higher the infection rate and the rate of production of Aspergillus flavus. Therefore, the freshly harvested peanuts must be dried as soon as possible so that the water activity of the peanuts falls within the safe water activity. Mature peanuts should be harvested in time, because delaying the peanut harvest time is also the reason for increasing the probability of peanuts infected with Aspergillus flavus. Finally, when peanuts are harvested, good storage conditions are the greatest guarantee of reducing the chance of infection with aflatoxin. A good storage environment includes certain ambient temperature, humidity, storage time, and oxygen content in the air. Food containing aflatoxin Foods containing aflatoxin can be divided into four major categories: peanut and peanut foods, vegetable oils and fatty foods, legumes and legumes, and other types of foods. Grains include rice, flour, corn, millet, buckwheat, and sorghum. Color and toxicity of aflatoxin Aspergillus is generally yellow, but it is hard to see with the naked eye. However, under ultraviolet irradiation, aflatoxin can produce blue-violet and green glitter. At the same time, aflatoxin is colorless, odorless and odorless. Aflatoxin b1 is the most toxic, and low dose intake can cause chronic poisoning. Its toxicity is 75 times stronger than diamine, 68 times stronger than arsenic. The great toxicity is chilling. Aflatoxin hazards The dangers of aflatoxin mainly include nausea, vomiting, jaundice, liver pain, and gastrointestinal bleeding, which seriously affect people's lives and work. This is the symptom of people after eating aflatoxin. When pigs are infected with Aspergillus flavus, which is a swine aflatoxin poisoning, it causes miscarriage, birth defects, and stillbirth in sows. The boar's libido declines, and the quality of excreted sperm is not high. At the same time, the internal organs and organs of livestock and poultry will be damaged, and teratogenicity may occur. After the poisoning of the pigs, they showed mental atrophy, walking, normal body temperature, dry stools, low head descent or standing still. When the above symptoms of swine appear, we should save it in time. The best way to control aflatoxin is the most timely and effective method is to give the pig 25% glucose (20mL/branch) + Vc 5 (2mL/branch) for 3~4d intravenous injection, or directly With glucose + Vc infusion; Another method is to mung bean 50g, licorice 20g Jianshui mixed feed, or put it into the sink for self-drinking, once every 7 ~ 10d. White sugar mixed feed, 20g per head, 2 times a day, continuous use 7 ~ 10d, better effect. Shijiazhuang Shangzu Building Materials Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.shangzuchem.com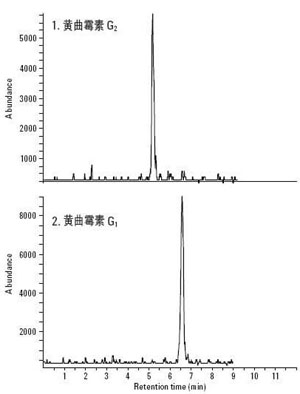
October 13, 2023